Documentation
InterDiode helps you to comfortably work a proper disconnected network. InterDiode gathers many resources from the internet and make them available on your internal, secured, network. You need two InterDiode servers, the first one being connected to the Internet and pushing downloaded data to the second, offline, server.
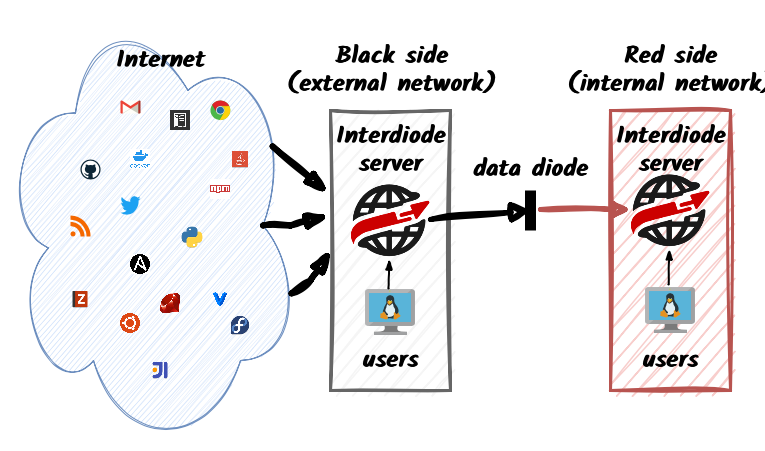
InterDiode copies programming language repositories, documentation, emails, or RSS feeds along with their linked web pages. All data is transferred through a data diode; you can either use your own data diode protocol or utilize the built-in one. With Interdiode:
USB keys will no longer move back and forth between your secured network and the internet,
Packages will be up-to-date,
Developers will be happier and more productive with a better environment :)
Of course, a complete authorization system is provided, allowing only power users to select which data is gathered and transferred to your red network.
Documentation content
Main features

classical programming languages and packaging systems:
APT (Debian/Ubuntu) packages,
Yum/DNF (RedHat/CentOS/Fedora) packages,
APK (RAlpine) packages,
Java/Python/Ruby/JavaScript/Rust libraries.
sysadmin/devops tools:
Ansible roles,
Docker containers,
Vagrant boxes,
git repositories,
documentations from ReadTheDocs or Zeal/Dash.
misc. internet resources:
GPG keys,
Twitter feeds,
Youtube/Vimeo/Dailymotion videos,
Wikipedia or StackOverflow dumps,
RSS/Atom feeds.
You can also receive emails, or periodically download arbitrary links.
InterDiode also comes with an integrated transfer protocol able to use physical datadiodes.
