Administration
Configuration check
First, you can display the loaded configuration values:
interdiode-ctl configuration show
And you can check if everything is valid:
interdiode-ctl configuration check
Testing connection
If you use the integrated Hairgap protocol, you can check if the connection between is working by running a receiver (on the red side) and sending a file:
interdiode-ctl hairgap test-receive --port 54313
interdiode-ctl hairgap test-send $SOME_RANDOME_FILENAME --port 54313
If all services are shut down, you can omit the port (useful to check if the right port is open). If data are transferred but test messages are not received, check if the shared secret is the same on both instances.
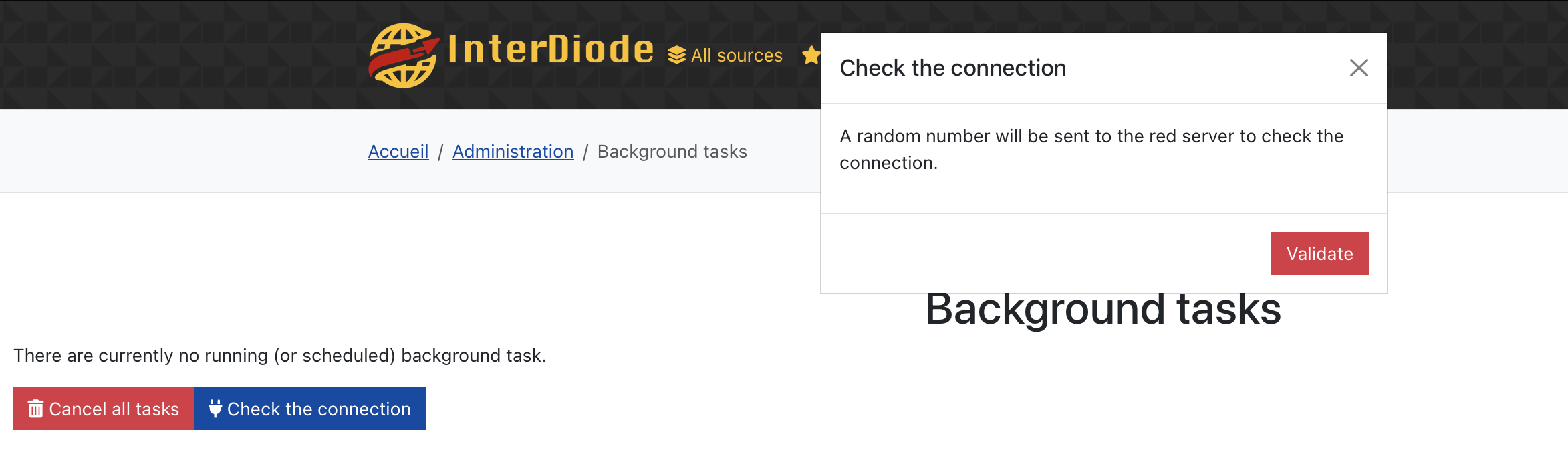
Even if you do not use the integrated protocol, you can send a simple test message from the Administration / background tasks page. This test message is a random test number. As soon as it is received by the red server, a popup should be displayed (and displayed on the transfers page when using the Hairgap protocol).
Recovering from transmission errors
Since transmissions are made over a one-way channel, transmission errors cannot be detected by the black-side server.
However, each Hairgap transmission is given a unique identifier and is sent with the identifier of the previous one. So, as soon as a transfer is received by the red server, the red one is able to check if previous transfers have been also successfully received. A list of all transfers is available in the Administration / Transfers page.
A list of all update and transfer actions is available:
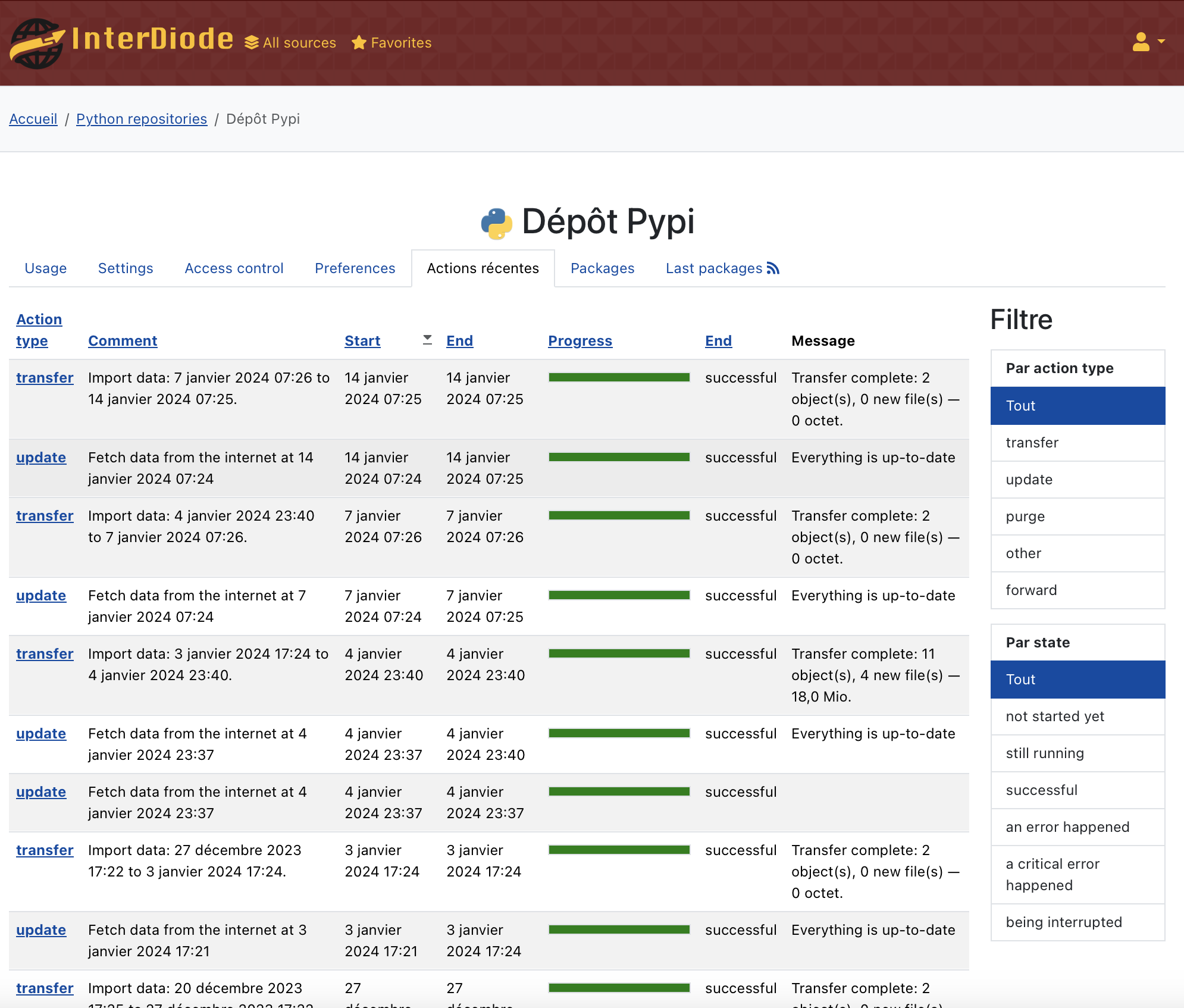
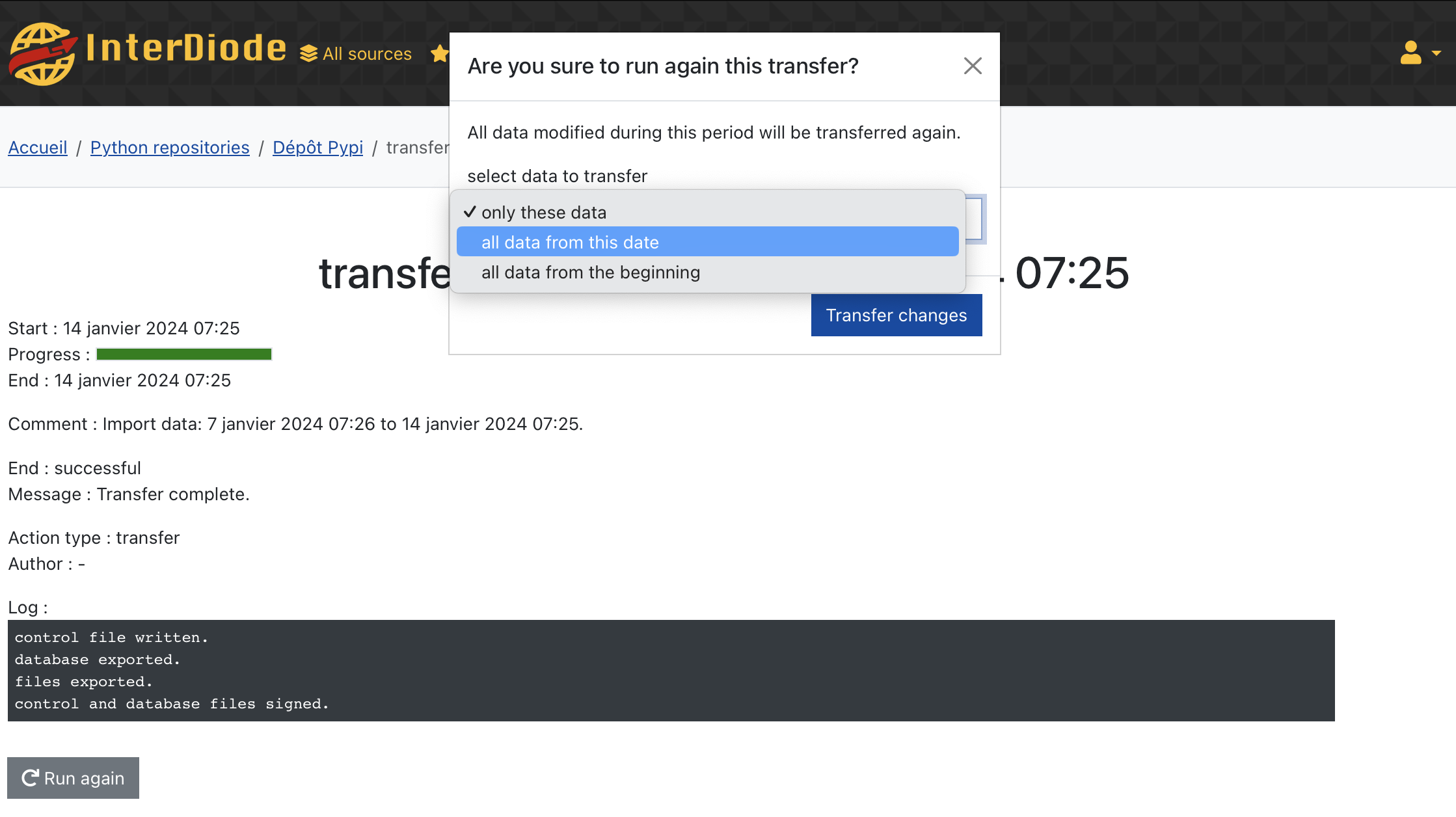
You can select the failed transfer to send data again. If several transfers are missing, you can choose to send all data modified from the first failed transfer, or even send again all data of the selected source.
When transmissions have been interrupted for a long time, you can trigger a new export of data of all sources:
interdiode-ctl source export '*' --background --first 2021-01-31T23:59:59Z+0000
Cleaning background task queues
If there are not enough workers for background tasks, like source updates, the number of waiting tasks can increase faster than the tasks can be processed, especially if some sources must be often updated, maybe every minute. In this case, the number of waiting tasks can be so huge that the best fix is to cancel all of them. Future scheduled updates will still happens, so nothing will be lost; updates will only be delayed.
On the contrary, you should not reset waiting transfer tasks; otherwise, you have to manually resend data to keep both black and red sides synchronized.
interdiode-ctl configuration reset --background --no-input
interdiode-ctl configuration reset --transfers --no-input
You can check the number of waiting tasks with the following commands:
redis-cli -h HOST -p PORT -n INTERDIODE_BROKER_DATABASE llen background
redis-cli -h HOST -p PORT -n INTERDIODE_BROKER_DATABASE llen hairgap
Cancelling running or interrupted actions
If an action has been interrupted for external reasons, the action can still be marked as running. This interrupted action can be manually marked as cancelled through the web interface. A command is also accessible through the command line interface for marking all interrupted actions as cancelled:
interdiode-ctl configuration reset --actions
A new update can be triggered on all updatable sources, followed by an export to the red side:
interdiode-ctl source update '*' --background
If some exports are also missing on the red side, new exports should have been triggered before triggering new updates.
User recovery
If you want to create another administrator, you can use the command line (or use the web interface to promote a regular user):
interdiode-ctl createsuperuser
Finally, you can change any password with another command:
interdiode-ctl changepassword [username]
Data integrity
If anything happens to your storage, you can check if files are still valid.
Corrupted files prevent black server to send data to the red server. The following command will check the integrity of each stored file
and remove corrupted ones. If you remove the --sha512 flag, only the size is checked. Beware that checking the integrity of large files can be very, very slow…
interdiode-ctl configuration check-files --sha512 --remove-corrupted
Secrets management
Debian and Ubuntu distribution require GPG-signed custom Aptitude repositories. InterDiode generates a new GPG key on the first start in a private GPG keychain. You can list available GPG keys (at least one should be then available), create a new one, select another key or export the public key block:
interdiode-ctl gpg list
interdiode-ctl gpg create
interdiode-ctl gpg export
interdiode-ctl gpg select
Moreover, a shared secret must exist between black and red instances: this allow your red instance to be sure that data have been sent by the right black instance. All transfers are signed by this secret.
[secrets]
shared_transfer_key = secret_key
Data backup
Everything is stored in:
the
[global]main_storage_directoryvalue of the configuration,the PostgreSQL database.
The Redis server is only used for transient data and you can safely lost its database: users will need to login again and some data sources may skip an update.
